Did you bring 'Fast Track to a 5' & a calendar?
Map out units
When's our first test?
Field Trip update & preliminary signup
Tardiness/absences...
5 minute break
Models of geologic time scale, tectonic plates, & earth's rotation/seasons
Notes: Earth Systems & Resources Part II
The Atmosphere
Earth's atmospheric composition:
The other gases are often referred to as trace gases.
Earth's atmosphere is about 300 miles thick but the densest part is within 18 miles of the
earth's surface.
Earth's atmospheric structure is characterized by differences in chemical composition that causes changes in temperature. The different layers of the atmosphere are:
The atmosphere influences both weather and climate.
Atmospheric Circulation is the large scale movement of air. More info
The Coriolis Effect The rotation of the Earth causes an interesting phenomena on free moving objects on the Earth. Objects in the Northern Hemisphere are deflected to
the right, while objects in the Southern Hemisphere are defected to the south. 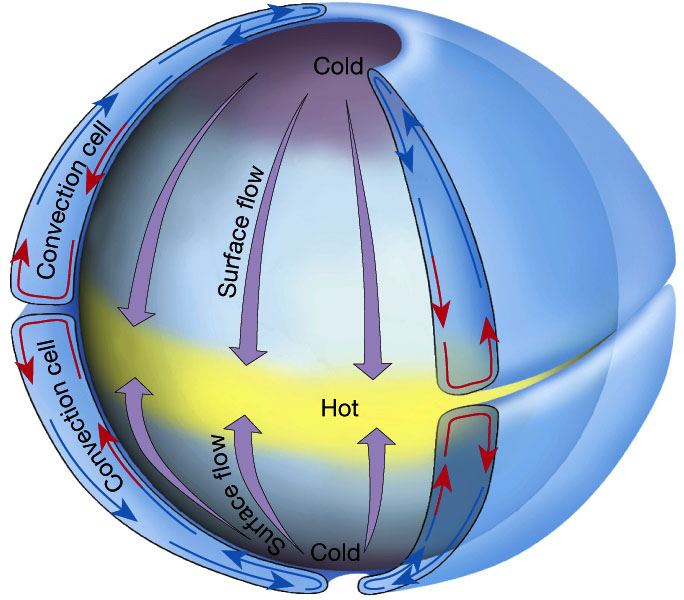
The main interaction between the atmosphere and ocean
is the transfer of energy through heat, moisture and momentum. They constantly react to each other, for example surface winds control the ocean currents.
ENSO or El Nino-Southern Oscillation is when prevailing trade winds blowing
westward either weaken or reverse. When El Nino happens it causes upwellings
to produce warm, less nutrient rich water. The winds also switch directions
causing changes in rainfall. |
Freshwater vs Saltwater
Ocean circulation is the large scale movement of waters in the ocean basins.
Winds drive surface circulation, and the cooling and sinking of waters in the polar regions drive deep circulation.Surface circulation carries the warm waters up towards the poles from the tropics. |
Soil and Soil Dynamics
The rock cycle is an idealized cycle of processes undergone by rocks in the earth's crust.
Soil formation depends on five major factors:
Go here to see the physical and chemical properties of soil. Main soils types are clay, sand and silt.
Soil erosion is the movement of soil components, especially topsoil, from one place to another usually by wind, flowing water, or both. This natural process can be greatly accelerated by human activities that remove vegetation from soil. |
Homework: watch Bozeman Science 'Atmosphere' video (11 mins) and answer:
-Explain the protocol passed in 1987
-What is the coriolis effect?


No comments:
Post a Comment